7 Powerful Electric Motors Transforming E‑Bikes: Ultimate Guide to Types, Capabilities, and Innovations
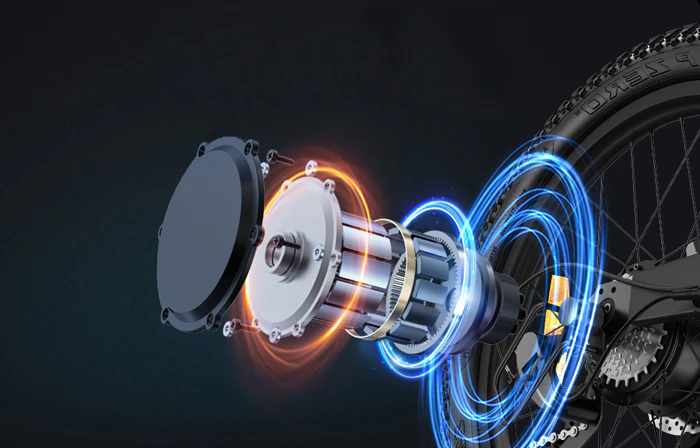
Electric Motors: Revolutionizing Power for E‑Bikes and Beyond
Electric motors are no longer just mechanical components—they are the driving force behind a global transformation in mobility and technology. From sleek e‑bikes and high-performance scooters to advanced electric vehicles and industrial robotics, electric motors are redefining what machines can do. Their ability to convert electrical energy into precise mechanical motion efficiently and reliably makes them indispensable in both personal and commercial applications.
The significance of Electrical Motors extends far beyond simple propulsion. They enable instant torque for rapid acceleration, quieter operation compared to internal combustion engines, and superior energy efficiency that maximizes battery life. For e‑bike enthusiasts, this means smoother rides, longer range, and the ability to tackle challenging terrain with minimal effort. For manufacturers and engineers, understanding the nuances of electric motors—including different motor types, power ratings, torque characteristics, and control systems—is essential for designing high-performance, sustainable, and future-proof solutions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the diverse world of electric motors, including hub motors, mid-drive motors, and brushless DC designs. We’ll examine their unique capabilities, ongoing technological improvements, and the remarkable innovations driving their evolution. Whether you are an e‑bike rider seeking the perfect setup, a hobbyist experimenting with DIY electric projects, or a developer in the EV industry, mastering the knowledge of electric motors opens doors to understanding the future of mobility and the potential of electrified transportation.
Choosing and optimizing electric motors for your e-bike requires precision, analysis, and the right digital tools.
These resources help you compare motors, estimate performance, simulate rides, and ensure your e-bike setup is both powerful and efficient.
- Compare Motors & Controllers — evaluate different motor types and controllers for optimal e-bike performance.
- Motor Power Estimator — calculate the ideal motor power for your riding style and terrain.
- Battery Pack Builder — design the perfect battery configuration to match your motor’s energy requirements.
- Charging Curve Simulator — simulate battery charge cycles and understand motor efficiency under different loads.
- Battery Discharge Curve Simulator — visualize how your battery and motor perform over long rides or steep climbs.
- E-Bike Consumption Calculator — estimate energy usage and riding range with your chosen motor setup.
- Custom E-Bike Firmware Builder — optimize motor performance and torque settings for your specific e-bike build.
Read More!
What Are Electric Motors?
Electric motors are sophisticated devices designed to convert electrical energy into precise mechanical motion, powering everything from small household gadgets to high-performance vehicles. Unlike traditional internal combustion engines that rely on fuel combustion, Electrical Motors provide instant torque, exceptional energy efficiency, and virtually silent operation, making them ideal for modern mobility solutions.
At their core, electric motors operate using the interaction between magnetic fields and electric current, creating rotational or linear motion that drives wheels, propellers, or machinery components. This efficiency not only reduces energy waste but also minimizes heat generation and maintenance requirements, providing a more sustainable and reliable alternative to conventional engines.
The versatility of electric motors is remarkable. They power electric bicycles (e‑bikes), scooters, drones, industrial automation systems, and even robotics, offering precise control over speed, torque, and direction. In e‑bikes, for example, electric motors enable smooth acceleration, assist riders on steep inclines, and extend battery range through optimized energy use.
As cities and nations worldwide prioritize clean energy and low-emission transportation, the global demand for efficient and compact electric motors continues to surge. Innovations in materials, motor design, and electronic controllers are expanding their potential, allowing lighter, more powerful, and longer-lasting motors. This trend highlights the crucial role of electric motors in shaping the future of sustainable mobility, smart infrastructure, and electrified personal transportation.
Types of Electric Motors
The world of Electrical Motors is diverse, with each type engineered for specific applications, efficiency, and performance requirements. Understanding the different types of electric motors is essential for riders, engineers, and enthusiasts who want to maximize power, range, and reliability in e‑bikes, scooters, and other electric vehicles.
1. Brushless DC Motors (BLDC)
Brushless DC motors (BLDC) are among the most popular electric motors for modern e‑bikes and small electric vehicles due to their superior efficiency, reliability, and low maintenance. Unlike brushed DC motors, BLDC motors operate without physical brushes, which eliminates friction and wear points, reducing heat loss and extending motor lifespan. These motors are highly responsive, delivering instant torque at low speeds, which makes them ideal for uphill climbs, city commuting, and rapid acceleration scenarios.
Key advantages of BLDC motors include:
- Exceptional energy efficiency and high power density
- Low operational noise and minimal heat generation
- Extended service life due to the absence of brushes
- Precise speed and torque control using electronic controllers
2. Hub Motors
Hub motors are another prevalent type of electric motors, integrated directly into the wheel hub. They are widely used in consumer e‑bikes because they simplify installation, reduce mechanical complexity, and offer smooth, quiet operation. Hub motors come in two main configurations: front hub and rear hub. Rear hub motors provide better traction, stability, and handling, while front hub motors are easier to retrofit into existing bicycles.
Despite their convenience, hub motors add unsprung weight to the wheel, which can slightly impact suspension performance and ride comfort. Nevertheless, they remain a cost-effective, low-maintenance solution for casual riders and urban commuters.
3. Mid‑Drive Motors
Mid-drive motors are positioned near the bicycle’s crankset, directly transferring power through the chain and gears. This design allows the motor to leverage the bike’s gear system for optimal torque and efficiency, especially on steep hills or challenging terrain. Mid-drive motors are often favored in performance-oriented e‑bikes because they provide better weight distribution, enhanced climbing ability, and more natural riding dynamics.
Although typically more expensive than hub motors, mid-drive electric motors offer significant advantages:
- Superior torque control for uphill and off-road riding
- Improved weight balance and handling
- Extended battery range through efficient gear-assisted power delivery
- Compatibility with advanced e-bike control systems and regenerative braking
Other specialized types of Electrical Motors, such as geared hub motors, outrunner motors, and axial flux designs, are emerging as technology advances. These innovations aim to maximize efficiency, reduce weight, and provide higher power outputs without compromising durability.
By understanding the characteristics and benefits of each type of electric motors, riders and engineers can make informed decisions to match motor choice with riding style, terrain, and performance goals.
Key Capabilities of Electric Motors
Electric motors have undergone remarkable advancements in recent years, offering unprecedented power, responsiveness, and energy efficiency. These capabilities are transforming not only e‑bikes and scooters but also electric vehicles, industrial machinery, and robotics. Understanding the core strengths of electric motors helps riders, engineers, and innovators maximize performance, longevity, and energy usage.
Instant Torque Delivery
One of the defining capabilities of electric motors is their ability to provide instant torque from zero RPM. Unlike internal combustion engines, which must build revolutions per minute to reach peak torque, Electrical Motors deliver immediate power the moment the rider engages the throttle. This instant response allows e‑bikes to accelerate rapidly, handle steep inclines effortlessly, and offer smooth and responsive rides in urban traffic or off-road conditions.
High Efficiency Ratings
Modern electric motors achieve efficiency levels often exceeding 90%, meaning the majority of electrical energy is converted into mechanical motion with minimal waste heat. High-efficiency motors not only reduce energy consumption but also directly impact battery performance. For e‑bikes and electric scooters, this translates to longer ride times, extended range, and more consistent power delivery, even during heavy load or challenging terrain.
Precision Modularity and Control
Another remarkable feature of advanced Electrical Motors is their modularity and sophisticated control systems. Modern motor controllers, often integrated with microprocessors and AI-powered algorithms, allow dynamic adjustment of torque, speed, and power delivery based on riding conditions. Features like regenerative braking are now common, enabling the motor to recover energy during deceleration and recharge the battery, further enhancing efficiency. Additionally, some systems offer customizable riding modes, traction control, and automatic torque distribution, making electric motors highly adaptable for diverse applications.
Scalability and Integration
Electric motors are highly scalable, which allows them to be integrated into a wide range of platforms—from lightweight commuter e‑bikes to heavy-duty cargo bikes, industrial robots, and electric cars. Their compact design and ability to interface seamlessly with batteries, controllers, and sensors make them versatile tools for innovation. As battery technology and electronic control systems continue to improve, the capabilities of electric motors will expand, providing higher power output, smoother performance, and longer operational life.
Reliability and Low Maintenance
Due to fewer moving parts compared to traditional engines, electric motors are inherently more reliable and require less maintenance. Brushless designs, in particular, minimize wear and tear, reduce overheating, and extend service life. This reliability is crucial for e‑bikes and industrial applications where consistent performance is essential.
Overall, the key capabilities of electric motors—instant torque, high efficiency, precise control, scalability, and reliability—position them as the cornerstone of modern electric mobility and industrial innovation. As technology advances, these motors will continue to redefine what is possible in sustainable transportation and smart machinery.
Recent Innovations in Electric Motor Technology
The field of electric motors is evolving at an unprecedented pace, driven by the demand for higher efficiency, greater power density, and more sustainable mobility solutions. Recent innovations are not only improving performance but also expanding the possibilities of e‑bikes, scooters, electric vehicles, and industrial machines. Understanding these technological advances is essential for riders, engineers, and developers seeking to leverage the full potential of electric motors.
1. Higher Torque Magnetic Materials
One of the most significant advancements in electric motors is the development of high-torque magnetic materials. Rare-earth alloys, such as neodymium-iron-boron, and advanced composite magnets provide substantially stronger magnetic fields, allowing motors to generate higher torque and power density without increasing size or weight. This breakthrough enables e‑bikes to accelerate faster, climb steeper hills, and carry heavier loads without compromising battery efficiency. Additionally, the increased magnetic efficiency reduces energy loss and heat generation, further improving motor lifespan.
2. Integrated Cooling Systems
Modern electric motors often incorporate sophisticated cooling technologies, including liquid cooling, forced air channels, and optimized thermal pathways. Efficient thermal management ensures that motors can sustain higher power output over extended periods without overheating. This innovation is critical for heavy-duty e‑bikes, cargo bikes, and commercial electric vehicles, where consistent high performance is required. Effective cooling also protects sensitive electronic components, extending the overall lifespan of the motor system.
3. Sensorless Motor Control
Another key innovation in electric motors is sensorless control technology. Traditional motors rely on physical sensors to detect rotor position, which adds cost, mechanical complexity, and potential points of failure. Sensorless control uses advanced algorithms and real-time feedback from voltage and current measurements to accurately determine rotor position, enabling precise torque and speed control without extra hardware. This not only reduces manufacturing costs but also enhances reliability, performance, and smooth operation under variable loads.
4. Lightweight and Compact Designs
Recent innovations focus on reducing weight and size while maintaining or increasing power output. Advances in motor winding techniques, materials, and structural design allow electric motors to be more compact and lighter, which is especially beneficial for e‑bikes and drones. Lightweight motors improve handling, acceleration, and energy efficiency, making electric vehicles more agile and extending battery life.
5. Smart and Connected Motor Systems
The integration of IoT and smart electronics into electric motors is another major trend. Connected motor systems can monitor performance, predict maintenance needs, and dynamically optimize power delivery based on riding conditions. For e‑bikes, this means real-time adjustment of torque and speed, adaptive regenerative braking, and even remote diagnostics, enhancing both rider experience and motor longevity.
These innovations collectively demonstrate the incredible potential of electric motors to revolutionize transportation and industrial applications. As materials, cooling methods, control systems, and connectivity continue to improve, electric motors will become even more powerful, efficient, and adaptable, driving the next generation of sustainable mobility.
The Future Potential of Electric Motors
The future of electric motors is incredibly promising, with their applications set to extend far beyond personal mobility into areas that redefine transportation, industry, and energy systems. As technology advances, electric motors are becoming more efficient, powerful, and adaptable, opening doors to innovations that were previously unimaginable.
One of the key growth areas for electric motors is in sustainable energy and grid solutions. By integrating with advanced energy storage systems (energy storage integration), these motors can help stabilize electrical grids, store renewable energy, and optimize power distribution. This not only enhances the reliability of clean energy systems but also positions electric motors as essential components in the global shift toward sustainable infrastructure.
Autonomous robotics is another frontier where electric motors will play a transformative role. High-precision motors allow robots to move with greater accuracy, efficiency, and responsiveness. From warehouse automation to delivery drones, the combination of electric motors and intelligent control systems will enable smarter, faster, and more energy-efficient robotic operations.
In industrial systems, electric motors are evolving to meet the demands of heavy-duty applications. Innovations in high-torque materials, thermal management, and sensorless control allow motors to sustain higher loads for longer periods while maintaining efficiency and reliability. This is particularly relevant for electrified manufacturing equipment, automated vehicles, and cargo transport solutions.
Battery technology will continue to amplify the potential of electric motors. Solid-state batteries, fast-charging chemistries, and higher-capacity lithium-ion variants will reduce energy constraints, allowing motors to deliver higher output with lighter, more compact designs. For e‑bikes and personal mobility devices, this means longer ride times, faster acceleration, improved climbing ability, and extended range—even on steep or rough terrain.
Looking further ahead, emerging technologies such as AI-driven motor control, predictive maintenance systems, and integrated IoT connectivity will make electric motors smarter than ever. These innovations will enable real-time optimization of torque, speed, and energy use, creating highly efficient, adaptive, and reliable electric vehicles and machinery. The combination of advanced motor design, improved battery technology, and intelligent control systems positions electric motors as central to the future of sustainable mobility, autonomous systems, and electrified industry worldwide.
Electric Motor Selection Guide for E‑Bike Builders
Choosing the right electric motors is one of the most critical decisions for any e‑bike project. The performance, efficiency, and overall riding experience depend heavily on selecting a motor that matches your riding style, terrain, and battery system. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you make the best choice:
1. Power Output
The power output of electric motors, measured in watts, directly impacts acceleration, top speed, and load-carrying ability. Higher wattage motors deliver stronger and faster acceleration, making them ideal for hilly terrain or heavy riders. However, more powerful motors draw more energy, which can reduce battery range. For commuting and casual rides, a moderate 250–500W motor is often sufficient, while high-performance setups may require 750–1,000W or more.
2. Torque
Torque is the rotational force that determines how well your electric motors handle inclines, heavy loads, and start-stop conditions. Mid-drive motors generally provide higher torque than hub motors because they leverage the bicycle’s gear system, offering better climbing ability and smoother power delivery. If you frequently ride on steep hills, carry cargo, or tow trailers, prioritizing torque is essential for a reliable and enjoyable ride.
3. Weight and Placement
The placement of electric motors affects handling, stability, and ride comfort. Hub motors are integrated into the wheel and add unsprung weight, which can slightly affect suspension performance. Mid-drive motors, positioned near the crankset, distribute weight more evenly, improving balance and maneuverability. Consider the overall weight of your motor system and how it interacts with the bike’s frame and battery to optimize ride dynamics.
4. Compatibility
Before selecting electric motors, ensure they are compatible with your battery voltage, controller, and frame. Voltage mismatches can reduce efficiency, damage components, or limit performance. Advanced motor controllers allow fine-tuning of torque, regenerative braking, and riding modes, so matching your motor with compatible electronics is crucial for achieving the best performance and efficiency.
5. Efficiency and Riding Conditions
High-efficiency electric motors convert more electrical energy into motion, extending battery life and increasing range. Consider the typical riding conditions: urban commuting, off-road trails, or cargo hauling. Motors optimized for specific use cases can provide smoother performance, better heat management, and longer component lifespan.
6. Noise and Maintenance
Brushless Electrical Motors are generally quieter and require less maintenance than brushed designs, making them ideal for long-term use. Evaluate your willingness to perform regular maintenance and whether a low-noise, durable motor is important for your daily ride.
By carefully evaluating these factors—power, torque, weight, placement, compatibility, efficiency, and maintenance—you can select the ideal electric motors for your e‑bike. Whether your goal is smooth city commuting, adventurous off-road riding, or heavy-duty cargo transport, understanding these considerations ensures a safe, efficient, and enjoyable electric bike experience.
Suggested topics:
10 Mistakes to Avoid When Buying electric bikes
Complete U.S. E-Bike Laws Guide
E-Bikes and Batteries Recycling
AI and Smart Sensors
Smart Urban Riding Etiquette
🎥 Watch: A clear and animated breakdown of how electric motors work — from electromagnetism to motion — perfect for readers looking to understand the fundamentals behind the motors powering e‑bikes and electric mobility. :contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
Conclusion
Electric motors are a cornerstone technology driving the global transition toward sustainable, efficient, and intelligent mobility. Their applications now span far beyond simple transportation, powering everything from lightweight commuter e‑bikes to high-performance electric vehicles, industrial automation, and advanced robotics. The ongoing evolution of electric motors continues to improve efficiency, torque delivery, reliability, and adaptability, making them more versatile than ever before.
Understanding the different types of Electrical Motors, including hub motors, mid-drive systems, and brushless designs, allows riders, engineers, and hobbyists to choose the ideal motor for their needs. Staying informed about key capabilities such as instant torque, high efficiency, precise control, and modular integration ensures optimal performance across a variety of applications—from urban commuting to off-road adventures and cargo transport.
Moreover, the latest innovations in electric motors—including advanced magnetic materials, integrated cooling, sensorless control, and smart IoT-enabled systems—signal a future where motors are lighter, more powerful, and more intelligent than ever. Coupled with advancements in battery technology, these improvements promise longer range, higher output, and an overall more sustainable and enjoyable riding experience.
By leveraging this knowledge, builders and riders can not only select the most suitable electric motors but also contribute to the larger movement toward clean, efficient, and high-performance electric mobility. The future of transportation is electrified, and electric motors lie at its very core, redefining what is possible in both personal and industrial mobility.
For deeper insights into choosing and optimizing Electrical Motors for your projects, explore the RideWattly Electric Bike Guide and our comprehensive reviews, where you’ll find expert advice, tutorials, and up-to-date information on the latest motor technologies.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Electric Motors for E-Bikes
What are electric motors and how do they work?
What types of electric motors are used in e-bikes?
What is the difference between hub motors and mid-drive motors?
How does torque affect e-bike performance?
Why are brushless electric motors preferred?
What recent innovations are improving electric motors?
How do electric motors affect battery life?
What should I consider when selecting an electric motor for my e-bike?
Can electric motors be used beyond e-bikes?
What is the future potential of electric motors?






